Understanding Air Quality Index (AQI)

The Air Quality Index (AQI) serves as a standardized tool to communicate the quality of air in a specific location. It synthesizes complex environmental data regarding various pollutants into a single value, making it easier for the public to understand air safety. The AQI is calculated based on the concentrations of several harmful pollutants, including particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ground-level ozone (O3), carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Each of these pollutants is assigned a numerical value that corresponds to predetermined health standards.
The AQI scale typically ranges from 0 to 500, categorized into different levels that indicate potential health effects. Values of 0-50 fall within the “Good” range, presenting little or no risk. As the AQI increases, it enters the “Moderate” (51-100), “Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups” (101-150), “Unhealthy” (151-200), and “Very Unhealthy” (201-300) classifications. An AQI above 300 is categorized as “Hazardous,” warning the general public to limit outdoor activity. Understanding these classifications is crucial for individuals, particularly vulnerable populations such as children, elderly individuals, or those with pre-existing health conditions.
Health implications are associated with various AQI readings. For instance, a moderate AQI can lead to respiratory issues in sensitive individuals, while high levels of pollution (AQI above 150) may affect everyone, increasing risks for heart and lung diseases. Therefore, monitoring air quality is essential for public health and safety, especially in regions like Lahore, known for fluctuating air quality. This alert system not only enhances public awareness but also enables individuals to take proactive measures to reduce their exposure to harmful air pollutants.
The 299 AQI Record in Lahore, 28th October, 2024

On October 28, 2024, Lahore recorded a remarkable Air Quality Index (AQI) of 299, positioning it among the cities with the most alarming pollution levels globally. This figure is indicative of hazardous air quality, which significantly escalates health risks for the city’s inhabitants. At this level, the air is classified as “Very Unhealthy,” triggering warnings for sensitive groups such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
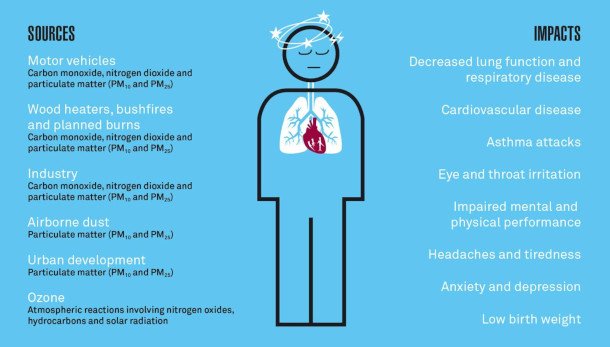
The primary contributors to such a high AQI in Lahore can be traced to multiple sources. Industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and construction activities are prevalent in the region, exacerbating the situation. Additionally, seasonal factors, particularly during the autumn months, have been known to worsen air quality. The use of crop burning in surrounding agricultural areas releases substantial particulate matter into the atmosphere, which subsequently settles over Lahore, further increasing the concentration of harmful pollutants.
Other contributing factors include the geographical and meteorological conditions unique to Lahore. The city experiences temperature inversions, which trap pollutants close to the ground level, preventing dispersal into the upper atmosphere. This situation is compounded by the dense urban population and associated energy consumption, leading to elevated emissions. Urban planning issues, such as inadequate green spaces and inefficient waste management practices, also play a significant role in maintaining high pollution levels.
Understanding the implications of a 299 AQI is crucial for public health awareness. Residents are advised to minimize outdoor activities, wear masks, and employ air purifiers within their homes to mitigate exposure to pollutants. It is vital for the local government and citizens to engage in sustainable practices and policies to address the roots of such high pollution levels, aiming for a healthier environment.
Health Impacts of Poor Air Quality